-
4 years ago
-

0
-
Blockchain
Introduction
Blockchain technology is a certain way of recording and confirming transactions. In this method, instead of a centralised platform, each of the participants have a complete record of the transactions achieved through a peer–to–peer verification of the transactions. Hence, there is no central recording system but it is up to each participant to keep a record of the transactions made. This system is also followed while operating Bitcoin with no central body.
Blockchain has the capacity to change the entire landscape of the trade finance industry. It can effectively lessen disputes and fraud while enabling transparency in trade asset movement and the flow of trade receivables. Indeed, Blockchain can lead to increased collaboration and better governing of trade transactions.
Description
A block is the “current” part of a Blockchain. It records all recent transactions and once this is complete, the block enters the Blockchain as a permanent database. Whenever a block is completed, a new one is generated. The Blockchain consists of an innumerable number of blocks, which are all joined to each other in a linear and chronological order. Characteristically, every block has a hash of the previous block. The Blockchain contains complete information about the user addresses of different people as well as their balances from the genesis block to the last completed block.
The Blockchain was created to make the transactions immutable, such that they cannot be deleted. Each block is added by cryptography, which precludes any meddling or interference. The system enables the distribution of data but negates any chances of the copying of data.
Advantages
- Offers greater security
As the Blockchain stores data throughout its network, it omits the risks that accompany data being held centrally. The Blockchain system does not have centralized points of vulnerability than can possibly be hacked. While we usually rely on the system of “username/password”, this has its loopholes. If the server security is weak, anyone can break into the database and get access to the passwords. However, Blockchain security methods employ encryption technology by virtue of which the data stored in it is incorruptible.
- Facilitates a well–connected network
With the Blockchain technology, users can directly transact with one another. This leads to an increased number of transactions. Therefore, Blockchain effectively provides the web with a new level of functionality.
- Causes immediate settlement of trade transactions
Blockchain entails peer confirmation of trades, which ensures that settlement of trades is instantaneous. The complications and hassles involved are automatically reduced.
- Provides transparency of trade transactions
Since all participants have a complete record of the transactions, the scenario of the equity market is absolutely transparent to them. This nullifies chances of altering previous transactions or falsifying transactions. If a false trade happens to take place, the participants will find inconsistencies in their ledger and will, thus, be able to reject the trade.
- Generates cost savings
The adoption of distributed ledger technology (DLT) in Blockchain enables banks and businesses to significantly cut costs. It mainly generates savings in three areas:
- In terms of maintenance, electronic ledgers are easier to maintain compared to traditional accounting systems. As trades are settled by peer confirmation, there is no need for a clearing house, auditors to verify trades and custodians to see that a fund has the shares that traders claim to hold. This omits the middlemen involved, which saves expenses.
- An almost fully automated DLT system causes far fewer errors and eliminates the need for repetitive confirmation steps. The occurrence of less number of errors reduces the costs for rectification.
- The Blockchain system minimizes the processing delay. This leads to less capital that is subject to the risk of pending transactions.
Challenges
- Operation is somewhat wasteful
In the Blockchain, every Node runs in order to keep up the Consensus. This provides zero downtime, makes data stored on the Blockchain unchangeable and enables the system to tolerate extreme levels of faults. However, all this is wasteful as each note simply repeats a task to reach Consensus, which burns electricity and takes more time for execution.
- Entails higher costs
Blockchain networks typically require Nodes in order to run successfully. But many of the networks lack an adequate number of Nodes to enable widespread usage. This results in greater costs as Nodes seek higher rewards when they complete transactions in a scenario with supply and demand.
- Creates a larger size of the database
With the addition of each “block” to the chain, the size of the database increases. This results in the following:
- A smaller ledger as not every Node has the capacity to carry a whole copy of the Blockchain, which hampers the Consensus, immutability and other such things
- A more centralized system as a high barrier to entry to become a Node encourages greater amount of centralisation in the network, with larger players exercising more control
- Uncertainty in Blockchain currencies
Unlike traditional (Fiat) currencies such as USD, GBP and EUR that are linked to the value of their respective economies, the currency of Blockchains is subject to fluctuations. As trade markets are subject to limited regulations and are highly speculative in nature, they witness fluctuations that raise the transaction value. This entails risks when one is transacting from Fiat currencies into Blockchain currencies.
- Unchangeability of smart contacts
The Blockchain functions in such a way that once a smart contact is added, it becomes immutable and cannot be changed. This means that if there are flaws in the code, they will remain there forever. This makes it possible for hackers to exploit code flaws to transfer the contents of smart contacts to their own accounts. Given that the Blockchain is immutable, it can lead to the loss of a valuable amount of data.
- Creation of forks
Many Blockchains decentralise their decision–making. When Nodes change their software, there is the possibility of a “fork”, which creates significant uncertainty, as it can divide the Blockchain network into a lot of variants.
Conclusion
Blockchain technology can transform the trade landscape in the best possible manner. Though not without challenges, it can be used to address trade transparency, privacy and security concerns.
Source Links:
https://www.investopedia.com/terms/b/blockchain.asp
https://www2.deloitte.com/content/dam/Deloitte/global/Documents/grid/trade–finance–placemat.pdf
http://theconversation.com/how–blockchain–technology–is–about–to–transform–sharemarket–trading–53807
https://blockgeeks.com/guides/what–is–blockchain–technology/
file:///C:/ProgramData/pbtmp245.html
https://itstillworks.com/disadvantages–password–authentication–protocol–2895.html
Browse Categories
Featured Posts
 4 years ago
4 years ago
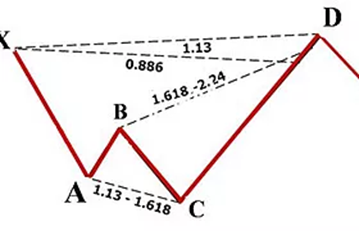
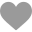
Cypher Pattern
 4 years ago
4 years ago
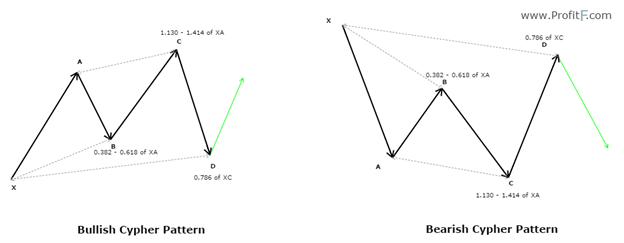
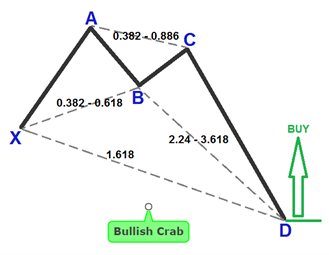
Crab Pattern
 4 years ago
4 years ago
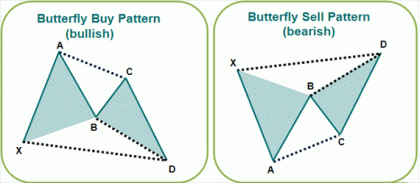
Butterfly Pattern
 4 years ago
4 years ago
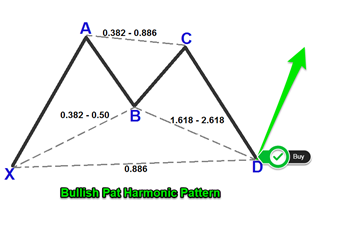
Bat Pattern
 4 years ago
4 years ago
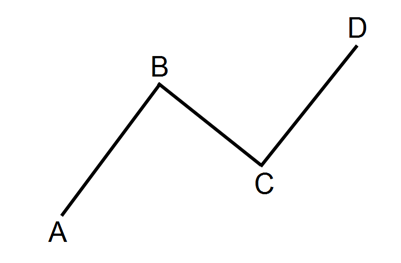
ABCD Pattern
 4 years ago
4 years ago
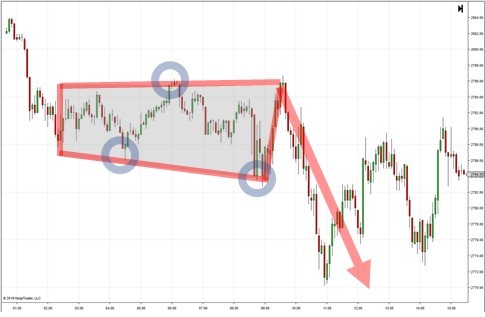
The Rectangle Pattern
 4 years ago
4 years ago
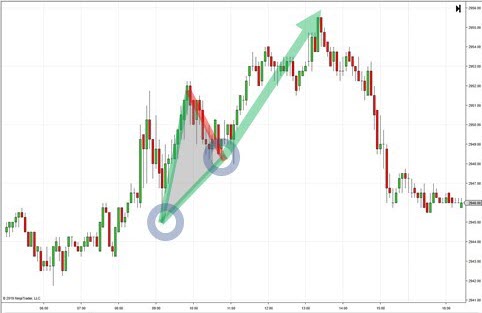
Triangle Patterns
 4 years ago
4 years ago
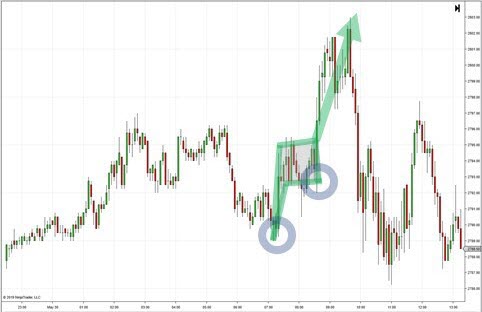
Flag Pattern
 4 years ago
4 years ago
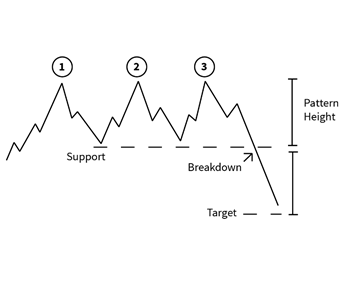
Double and Triple Pattern
 4 years ago
4 years ago
The Cup with Handle Pattern
 4 years ago
4 years ago
The Head-and-Shoulders Pattern
Popular Posts
Algorithmic Trading
4 years agoAn Overview of Initial Coin Offering (ICO)
4 years agoMonero Cryptocurrency
4 years ago